IoC 容器的对象生存期管理
如果你一直在使用 IoC 容器,你可能已经使用过了一些对象生存期管理模型(Object Lifetime Management)。通过对对象生存期的管理,将使对象的复用成为可能。同时其使容器可以控制如何创建和管理对象实例。
Unity 提供的对象生存期管理模型是通过从抽象类 LifetimeManager 的派生类来完成。Unity 将为每个类型的注册创建生存期管理器。每当 UnityContainer 需要创建一个新的对象实例时,将首先检测该对象类型的生存期管理器,是否已有一个对象实例可用。如果没有对象实例可用,则 UnityContainer 将基于配置的信息构造该对象实例并将该对象交予对象生存期管理器。
LifetimeManager
LifetimeManager 是一个抽象类,其实现了 ILifetimePolicy 接口。该类被作为所有内置或自定义的生存期管理器的父类。它定义了 3 个方法:
GetValue - 返回一个已经存储在生存期管理器中对象实例。
SetValue - 存储一个新对象实例到生存期管理器中。
RemoveValue - 从生存期管理器中将已存储的对象实例删除。UnityContainer 的默认实现将不会调用此方法,但可在定制的容器扩展中调用。
Unity 内置了 6 种生存期管理模型,其中有 2 种即负责对象实例的创建也负责对象实例的销毁(Dispose)。
TransientLifetimeManager - 为每次请求生成新的类型对象实例。 (默认行为)
ContainerControlledLifetimeManager - 实现 Singleton 对象实例。 当容器被 Disposed 后,对象实例也被 Disposed。
HierarchicalifetimeManager - 实现 Singleton 对象实例。但子容器并不共享父容器实例,而是创建针对字容器的 Singleton 对象实例。当容器被 Disposed 后,对象实例也被 Disposed。
ExternallyControlledLifetimeManager - 实现 Singleton 对象实例,但容器仅持有该对象的弱引用(WeakReference),所以该对象的生存期由外部引用控制。
PerThreadLifetimeManager - 为每个线程生成 Singleton 的对象实例,通过 ThreadStatic 实现。
PerResolveLifetimeManager - 实现与 TransientLifetimeManager 类似的行为,为每次请求生成新的类型对象实例。不同之处在于对象实例在 BuildUp 过程中是可被重用的。
Code Double
public interface IExample : IDisposable
{
void SayHello();
}
public class Example : IExample
{
private bool _disposed = false;
private readonly Guid _key = Guid.NewGuid();
public void SayHello()
{
if (_disposed)
{
throw new ObjectDisposedException("Example",
string.Format("{0} is already disposed!", _key));
}
Console.WriteLine("{0} says hello in thread {1}!", _key,
Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId);
}
public void Dispose()
{
if (!_disposed)
{
_disposed = true;
}
}
}
TransientLifetimeManager
TransientLifetimeManager 是 Unity 默认的生存期管理器。其内部的实现都为空,这就意味着每次容器都会创建和返回一个新的对象实例,当然容器也不负责存储和销毁该对象实例。
private static void TestTransientLifetimeManager()
{
IExample example;
using (IUnityContainer container = new UnityContainer())
{
container.RegisterType(typeof(IExample), typeof(Example),
new TransientLifetimeManager());
// each one gets its own instance
container.Resolve().SayHello();
example = container.Resolve();
}
// container is disposed but Example instance still lives
// all previously created instances weren't disposed!
example.SayHello();
Console.ReadKey();
}
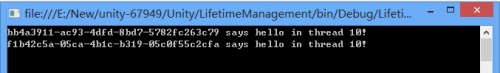
ContainerControlledLifetimeManager
ContainerControlledLifetimeManager 将为 UnityContainer 及其子容器提供一个 Singleton 的注册类型对象实例。其只在第一次请求某注册类型时创建一个新的对象实例,该对象实例将被存储到生存期管理器中,并且一直被重用。当容器析构时,生存期管理器会调用 RemoveValue 将存储的对象销毁。
Singleton 对象实例对应每个对象类型注册,如果同一对象类型注册多次,则将为每次注册创建单一的实例。
private static void TestContainerControlledLifetimeManager()
{
IExample example;
using (IUnityContainer container = new UnityContainer())
{
container.RegisterType(typeof(IExample), typeof(Example),
new ContainerControlledLifetimeManager());
IUnityContainer firstSub = null;
IUnityContainer secondSub = null;
try
{
firstSub = container.CreateChildContainer();
secondSub = container.CreateChildContainer();
// all containers share same instance
// each resolve returns same instance
firstSub.Resolve().SayHello();
// run one resolving in other thread and still receive same instance
Thread thread = new Thread(
() => secondSub.Resolve().SayHello());
thread.Start();
container.Resolve().SayHello();
example = container.Resolve();
thread.Join();
}
finally
{
if (firstSub != null) firstSub.Dispose();
if (secondSub != null) secondSub.Dispose();
}
}
try
{
// exception - instance has been disposed with container
example.SayHello();
}
catch (ObjectDisposedException ex)
{
Console.WriteLine(ex.Message);
}
Console.ReadKey();
}
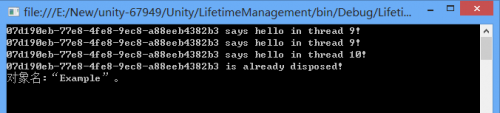
HierarchicalLifetimeManager
HierarchicalLifetimeManager 类衍生自 ContainerControlledLifetimeManager,其继承了父类的所有行为。与父类的不同之处在于子容器中的生存期管理器行为。ContainerControlledLifetimeManager 共享相同的对象实例,包括在子容器中。而 HierarchicalLifetimeManager 只在同一个容器内共享,每个子容器都有其单独的对象实例。
private static void TestHierarchicalLifetimeManager()
{
IExample example;
using (IUnityContainer container = new UnityContainer())
{
container.RegisterType(typeof(IExample), typeof(Example),
new HierarchicalLifetimeManager());
IUnityContainer firstSub = null;
IUnityContainer secondSub = null;
try
{
firstSub = container.CreateChildContainer();
secondSub = container.CreateChildContainer();
// each subcontainer has its own instance
firstSub.Resolve().SayHello();
secondSub.Resolve().SayHello();
container.Resolve().SayHello();
example = firstSub.Resolve();
}
finally
{
if (firstSub != null) firstSub.Dispose();
if (secondSub != null) secondSub.Dispose();
}
}
try
{
// exception - instance has been disposed with container
example.SayHello();
}
catch (ObjectDisposedException ex)
{
Console.WriteLine(ex.Message);
}
Console.ReadKey();
}
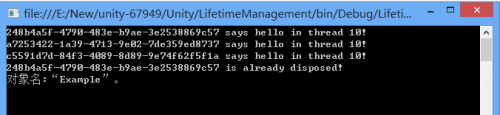
ExternallyControlledLifetimeManager
ExternallyControlledLifetimeManager 中的对象实例的生存期限将有 UnityContainer 外部的实现控制。此生存期管理器内部直存储了所提供对象实例的一个 WeakReference。所以如果 UnityContainer 容器外部实现中没有对该对象实例的强引用,则该对象实例将被 GC 回收。再次请求该对象类型实例时,将会创建新的对象实例。
private static void TestExternallyControlledLifetimeManager()
{
IExample example;
using (IUnityContainer container = new UnityContainer())
{
container.RegisterType(typeof(IExample), typeof(Example),
new ExternallyControlledLifetimeManager());
// same instance is used in following
container.Resolve().SayHello();
container.Resolve().SayHello();
// run garbate collector. Stored Example instance will be released
// beacuse there is no reference for it and LifetimeManager holds
// only WeakReference
GC.Collect();
// object stored targeted by WeakReference was released
// new instance is created!
container.Resolve().SayHello();
example = container.Resolve();
}
example.SayHello();
Console.ReadKey();
}
需要注意,在 Debug 模式下,编译器不会优化本地变量,所以引用有可能还存在。而在 Release 模式下会优化。
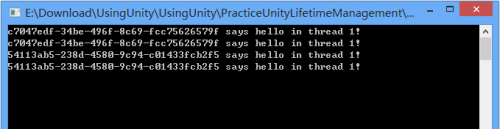
PerThreadLifetimeManager
PerThreadLifetimeManager 模型提供“每线程单实例”功能。所有的对象实例在内部被存储在 ThreadStatic 的集合。容器并不跟踪对象实例的创建并且也不负责 Dispose。
private static void TestPerThreadLifetimeManager()
{
IExample example;
using (IUnityContainer container = new UnityContainer())
{
container.RegisterType(typeof(IExample), typeof(Example),
new PerThreadLifetimeManager());
Actionaction = delegate(int sleep)
{
// both calls use same instance per thread
container.Resolve().SayHello();
Thread.Sleep(sleep);
container.Resolve().SayHello();
};
Thread thread1 = new Thread((a) => action.Invoke((int)a));
Thread thread2 = new Thread((a) => action.Invoke((int)a));
thread1.Start(50);
thread2.Start(50);
thread1.Join();
thread2.Join();
example = container.Resolve();
}
example.SayHello();
Console.ReadKey();
}
更多关于unity培训的问题,欢迎咨询千锋教育在线名师。千锋教育拥有多年IT培训服务经验,采用全程面授高品质、高体验培养模式,拥有国内一体化教学管理及学员服务,助力更多学员实现高薪梦想。



















 京公网安备 11010802030320号
京公网安备 11010802030320号